With the ever-increasing integration of cannabis into mainstream culture and its growing legality, it’s becoming harder than ever to deny the topic of cannabis as a medicine. In today’s world, we tend to associate any discussion of psychedelics with hippies, stoners, or even conspiracy theorists. But that’s far from the truth when it comes to cannabis. Cannabis is widely used globally as a recreational drug; however, there are also many medicinal uses for this plant. There are currently over 100 cannabinoids present in industrial amounts in the flowering tops of cannabis plants. These chemical compounds have different effects on everyone, but many people are interested in learning more about other substances found in the plant. If you have access to medical-grade CBD oil, you can use it as a healthy alternative to prescription medicines and over-the-counter drugs such as Tylenol or acetaminophen for example. Now let’s explore some of these cannabinoids and their effects to help you decide whether cannabis is the best option for your treatment.
Cannabidiol (CBD)
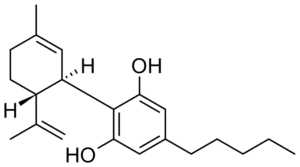
Cannabidiol also referred to as CBD, is a cannabis compound that has significant medical benefits without the euphoric effects of other cannabinoids. Unlike THC, CBD is not psychoactive and doesn’t produce the “high” associated with cannabis. However, that does not mean it can’t be used for medical purposes. In fact, many physicians recommend CBD oil for patients suffering from chronic pain and anxiety disorders. Marijuana edibles are also a great option for those looking to use CBD oil in food.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
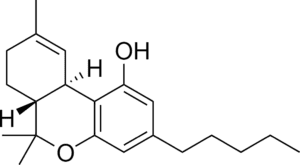
THC is the most well-known cannabinoid found in cannabis. It’s responsible for marijuana’s high and it’s also great for pain relief. THC works by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and body. These receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system, which helps to regulate things like mood, appetite, and pain. THC activates these receptors, leading to the various effects that people experience when they use marijuana. In addition to its psychoactive effects, THC is also a powerful analgesic, or pain reliever. It’s been shown to be effective in treating a variety of conditions, including chronic pain, cancer-related pain, and nerve pain. THC is also effective in reducing inflammation, making it a potential treatment for conditions like arthritis and Crohn’s disease. However, THC can also have some negative side effects, including anxiety and paranoia. As a result, it’s important to start with a low dose if you’re new to using marijuana.
Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (D9-THCV)
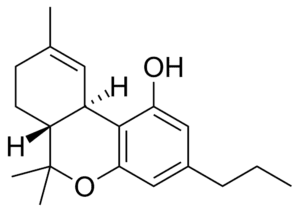
Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (D9-THCV) is a cannabinoid that is similar to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). However, D9-THCV has a propyl group rather than a pentyl group, which produces effects that are noticeably distinct from THC. While both cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system, D9-THCV binds more weakly to CB1 receptors than THC. This difference in binding affinity may contribute to the different effects of these two cannabinoids. For example, D9-THCV has been shown to reduce anxiety and convulsions, while THC may increase anxiety. Additionally, D9-THCV is a more potent inhibitor of cancer cell growth than THC. Therefore, further research on D9-THCV is warranted to elucidate its potential therapeutic applications.
Cannabigerol (CBG)
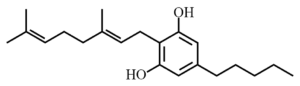
Cannabigerol, or CBG, is a minor cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. While most CBG (99%) is converted into other cannabinoids like THC and CBD during plant growth, some strains of cannabis produce larger quantities of CBG. Recent research has found that CBG may have neuroprotective properties and could be effective in treating Alzheimer’s disease. In a study exploring the therapeutic potential of various phytochemicals in neurodegenerative and gastrointestinal diseases, CBG was found to prevent loss of cell viability. This means that CBG could potentially help to protect cells from damage caused by Alzheimer’s disease. While more research is needed to confirm these findings, the results of this study suggest that CBG could be a promising treatment for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological disorders.
Additionally Cannabigerol is already marketed as a dietary supplement to help with inflammatory bowel disease, although more research is needed the compound does act as inhibitors of cytokine and 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin which are an essential part of the inflammatory process. Cytokines are a family of signaling proteins that play a role in cell signaling, and their overproduction has been implicated in a wide variety of inflammatory diseases. 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin is a cancer chemotherapy drug that inhibits DNA synthesis, and its overproduction has also been linked to inflammatory bowel disease. Therefore, cannabigerol’s ability to act as an inhibitor of these two compounds could potentially make it an effective treatment for inflammatory bowel disease. However, more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Cannabinol (CBN)
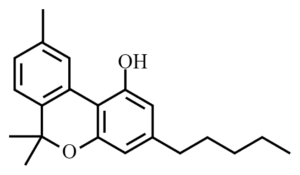
Although CBN is a minor cannabinoid, it nevertheless plays an important role in the overall effects of cannabis. Unlike THC, CBN is not primarily derived from the plant’s main psychoactive compound. Instead, it is found in trace amounts in aged and stored cannabis. Although it is only 10% as potent as THC, CBN is nonetheless psychoactive. It binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors, but has a higher affinity for CB2 receptors. This makes CBN an important player in the overall effects of cannabis. By binding to more selectivity to CB2 receptors, CBN helps to modulate the effects of THC. In this way, it helps to create the unique ‘entourage effect‘ that only cannabis can provide.
The entourage effect is a hypothesis that suggests that cannabis compounds other than tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) act synergistically with it to modulate the overall psychoactive effects of the plant. Researchers believe that this effect may explain why some people respond differently to cannabis than others. For example, CBD is thought to counteract some of the negative effects of THC, such as anxiety and paranoia. Some studies have shown that CBD can also increase the beneficial effects of THC, such as pain relief. The entourage effect is still being studied, but it may help to explain why certain strains of cannabis are more effective for certain conditions than others.
Other Cannabis Compounds
While THC is the most well-known cannabinoid, there are actually over 100 different cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. Other cannabis compounds have shown therapeutic potential as well. For example, cannabidivarin (CBDv) is known to be effective in reducing seizure activity due to its anticonvulsant effects. CBDv has also been shown to moderate the effects of THC, making it a promising candidate for use in medical marijuana formulations.
There is still much research that needs to be done to explore there 100+ cannabinoids but preliminary research shows promise for Cannabis compounds to be used in a variety of ways.
How to Stay Healthy When Using Cannabis as Medicine
While cannabis has been shown to be effective in treating a variety of medical conditions, it’s important to use it judiciously and under the care of a healthcare professional. As with any medication, there is the potential for side effects, so it’s important to start with a low dose and increase gradually as needed. It’s also important to be aware of the different methods of administration and choose the one that is best for you. Smoking marijuana can irritate the lungs, so vaporizing or using edibles may be a better option. Whatever method you choose, make sure you are using a high-quality product from a reputable source. Lastly, be sure to stay hydrated and take breaks if you feel any negative effects. By following these simple tips, you can use cannabis safely and effectively as medicine.
FAQs
What are the medicinal benefits of cannabis?
There are so many medicinal benefits of cannabis that I don’t know where to start. One of the best way to start is by explaining some of the most common health problems that sufferers of these conditions often have. IBS, Crohn’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Hepatitis C, Chronic Pain, Glaucoma, Epilepsy, Alzheimer’s Disease, Traumatic Brain Injury, Spinal Cord Injury (SCI), ALS/Muscular Dystrophy as well as many more are all being treated increasingly effectively with cannabis. I’m sure you may know some of them if you’ve met any of your friends that have one of those diseases. It’s not perfectly approved for treatment for everybody with those diseases yet but clinical trials are underway and hopefully, we’ll see the results soon! Anyway, so those are just some examples of the common issues people from around the world suffer from daily.
Now let me share with you a few facts about its medicinal uses:
- Cannabidiol (CBD) anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, anti-epileptical and anti-tumoral; reduces cell death via apoptosis in PC12 cells; protect kidney cells from oxidative stress; extends the lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster; expresion in C2C12 myoblast cells and BV-2 microglial cells (brain cells) suggest possible role in neurogenesis and immune regulation.
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in colonic carcinoma cell lines induce apoptosis through A20/SUK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase assays.
- Cannabigerol (CBG) in activation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK assays demonstrating endogenous cannabinoid-like activity in tissues from rats.
- Cannabichromene (CBC) binding affinity and modulation profile identical to THC dendritic receptors in mouse brain membranes.
- Cannabidivarin (CBDV) possesses at least two agonist stereoisomers.
How do cannabinoids work?
Cannabinoids are a class of active compounds that are found in the Cannabis plant. These molecules interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which is involved in a number of physiological processes, including pain perception, immune function, and appetite. When cannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors, they can modulate these processes and produce a variety of effects, both beneficial and adverse. For example, THC, the main psychoactive compound in cannabis, binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and produces the “high” associated with marijuana use. In contrast, CBD is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Cannabinoids can also be synthetic, as is the case with Marinol, a synthetic form of THC that is used to treat nausea and vomiting in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
What are the side effects of cannabis use?
While cannabis is often praised for its medicinal properties, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects of using this drug. Cannabis can cause dizziness, impaired coordination, and difficulty concentrating. It can also lead to anxiety, paranoia, and Panic attacks. Some people may also experience psychosis, a condition that causes them to lose touch with reality. In rare cases, people have been known to experience hallucinations and delusions after using cannabis. However, it is important to remember that everyone reacts differently to the drug, and not everyone will experience these side effects. If you are concerned about the potential risks of using cannabis, it is always best to speak with a medical professional before using the drug.
